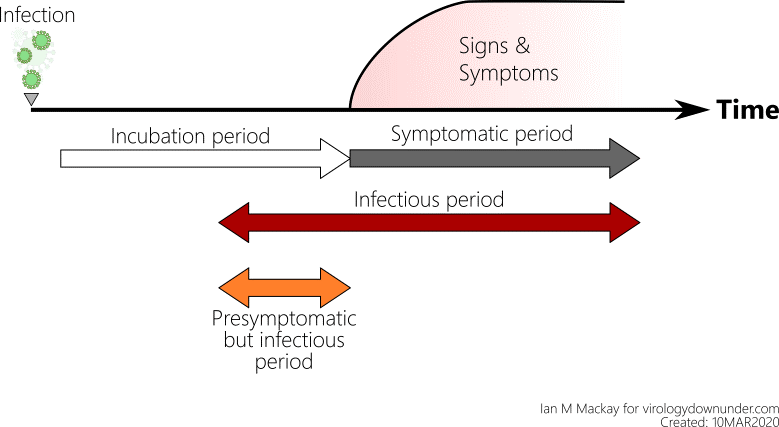
Determining the infectious period of COVID-19 is complicated by three factors:
- People can be diagnosed when they are symptomatic, pre-symptomatic, or asymptomatic,
- The standard diagnostic test, RT-PCR, is accurate for diagnosis as it can detect viral genetic material, but it cannot document when someone is no longer infectious because it cannot distinguish whether viral particles are still infectious or not,
- Cell culture is the best way to confirm whether an infectious Virus is present, but it takes time and requires specialized laboratory facilities.
- Symptoms of COVID 19 in mild cases include fever, sore throat, dry cough, malaise, and body aches or nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, loose stools. Acute respiratory distress syndrome, shock, coagulation defects, encephalopathy, heart and kidney failure in severe cases.